 If you’re like most people, you keep track of a lot of numbers — important numbers — not to mention passwords. I’ll apologize up front because I’m going to tell you about some more numbers you should know. They’re important because they tell you something about the state of your health.
If you’re like most people, you keep track of a lot of numbers — important numbers — not to mention passwords. I’ll apologize up front because I’m going to tell you about some more numbers you should know. They’re important because they tell you something about the state of your health.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
What BMI can tell you
BMI calculates body fat. It is a measure of your weight in proportion to your height. If your BMI is too high, you may be at increased risk for several chronic health problems, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, gall bladder disease, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea and cancer. All in all, BMI should give you a reasonable estimate of how much body fat you have. However, it may underestimate body fat if you have low muscle mass or overestimate it if you are extremely muscular. Another problem that might get overlooked is excess abdominal fat. Your BMI might be in the normal range, but if you have excess belly fat, you may be at increased risk of heart disease.
To figure out your BMI, use this calculator from the Mayo Clinic.
What the numbers mean
- Less than 18.5 Underweight
- 18.5 to 24.9 Normal
- 25 to 29.9 Overweight
- 30 or greater Obese
Waist measurement
What waist size can tell you
Excess belly fat is a greater risk factor for heart disease than excess fat in any other part of the body. You can have a normal BMI and still be abdominally obese.
What the CDC considers abdominally obese
Men: Waist measurement more than 40.2 inches.
Women: Waist measurement more than 34.6 inches.
How to measure
Wrap a tape measure around your waist, about the level of your belly button. While you’re at it, figure out your waist-to-hip ratio, which is the size of your belly compared to the size of your hips. Divide your waist measurement by your hip measurement. A ratio of 0.8 or lower is considered normal.
Cholesterol
What cholesterol can tell you
Our body’s need cholesterol to function normally, but if you’ve got high LDL (bad) cholesterol or low HDL (good) cholesterol, your arteries may become plugged with fatty plaques, which can put you at risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
What’s normal?
- Total cholesterol — Less than 200 mg/dL
- HDL cholesterol — Greater than 50 mg/dL
- LDL cholesterol — Less than 130 mg/dL (less than 100 mg/dL for those at high risk for heart disease)
When to test and how often
If you are age 20 or older and have not been diagnosed with heart disease, the American Heart Association recommends having your cholesterol levels checked every four to six years as part of a cardiovascular risk assessment. You should check with your doctor about your heart disease risk and how often you should be tested.
Triglycerides
What triglycerides can tell you
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood. The body converts calories it doesn’t need right away into triglycerides and stores them in fat cells. If you have high triglycerides, which can happen if you eat more calories than you burn, you can increase your risk of heart disease — especially if you also have high LDL cholesterol.
When to test and how often
It’s recommended that you get your triglycerides checked every time you have your cholesterol checked.
What’s normal?
- Normal — less that 150 mg/dL (the American Heart Association says 100 mg/dL is best.
- Borderline high — 150 to 199 mg/dL
- High — 200 to 499 mg/dL
- Very high — 500 mg/dL
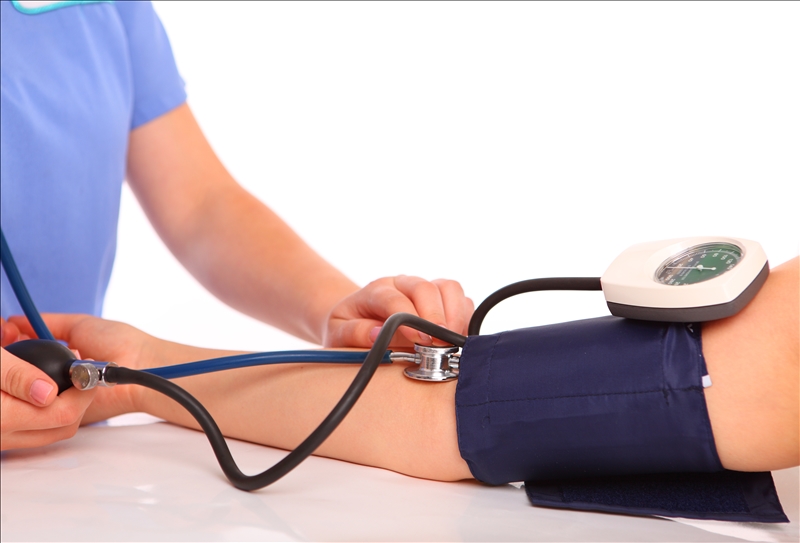
Blood pressure
What blood pressure can tell you
Blood pressure rises with each heartbeat and falls when your heart relaxes between beats. If your blood pressure is high it means your heart has to work harder, which increases your risk for heart disease, stroke, heart failure and kidney disease.
What the numbers mean
| Systolic (Top) | Diastolic (bottom) | Meaning | |
| Below 120 | and | Below 80 | Normal blood pressure |
| 120-139 | or | 80-89 | Pre high blood pressure |
| 140-159 | or | 90-99 | Stage 1 high blood pressure |
| 160 or more | or | 100 or more | High blood pressure |
When to check your blood pressure
According to the CDC, most people should have their blood pressure checked at each doctor visit, but at least every two years. If you have already been diagnosed with heart disease or have risk factors, it should be more closely monitored.
Blood sugar
What your blood sugar can tell you
If your blood sugar is high, it means that your body either isn’t making enough insulin or can’t properly use the insulin it does make, which could be a sign of diabetes or pre diabetes. Insulin helps move sugar (glucose) from the blood into cells. Over time and without any symptoms, high blood sugar can damage blood vessels, nerves, the kidneys and the eyes.
Who should have blood sugar checked?
Recommendations from the American Diabetes Association:
- Anyone with a BMI higher than 25, along with other risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol or history of heart disease.
- Anyone older than 45 should get an initial screening and if results are normal, be screened ever three years.
What’s normal?
A fasting glucose level or hemoglobin A1C can be done with a blood test during a routine physical. A glucose level of less than 100 mg/dL and an A1C of below 5.7 percent are considered normal.

Thanks for the piece on numbers. I had not done my BMI for some time…it is 22.2 and my waist is 32″. At my last physical the other numbers were good too.
You’re in great shape Russ. Must be clean living, bike riding and not having to punch a clock every day!